Summary: With ever-increasing workplace training costs, it is a challenge to devise a virtual training solution that is engaging for all employees. In this article, we will explore the effectiveness of gamification in eLearning to deliver unparalleled training experiences across all learning styles.
Also read latest article on Examples of Microlearning.
How To Deliver Effective eLearning Gamification
Τhe average spending on workplace training per employee worldwide in 2019 was $1308. The companies aim to carve out a training program that reduces the learning curve and increases ROI. A dynamic virtual training solution should cater to everyone’s training needs and learning styles.
The use of gamification in eLearning makes the corporate training module highly effective. It is found engaging by many employees irrespective of their learning style.
Gamification In eLearning
Let’s get to know about the gaming elements in eLearning. The common concepts are game-based learning and gamification, which are sometimes used interchangeably by many of us. However, there is a difference.
Game-based learning refers to an active learning experience within a game framework. In comparison, gamification is a process of incorporating game elements into the virtual training solution. Both game-based learning and gamification help to increase engagement and training outcomes.
“Play is our brain’s favorite way of learning,” said poet, essayist, and naturalist Diane Ackerman.
Therefore, it is not surprising that the majority of employees find gamification in eLearning more engaging and motivating. There is no better way of motivation than the experience of joy in what we do. The same applies to corporate learning and no other method can bring more joy than gamification.
But what makes gamification in eLearning a favorite among people with varied learning styles? We will take into consideration the VARK model to understand this aspect. Gamification caters to all learning styles as elucidated by the VARK model.
VARK Model
The VARK model identifies four main types of learners based on their learning styles: visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic. It was introduced by educational theorist Neil Fleming in 1987. VARK stands for Visual, Aural, Reading, and Kinesthetic. Let’s look into each of them.
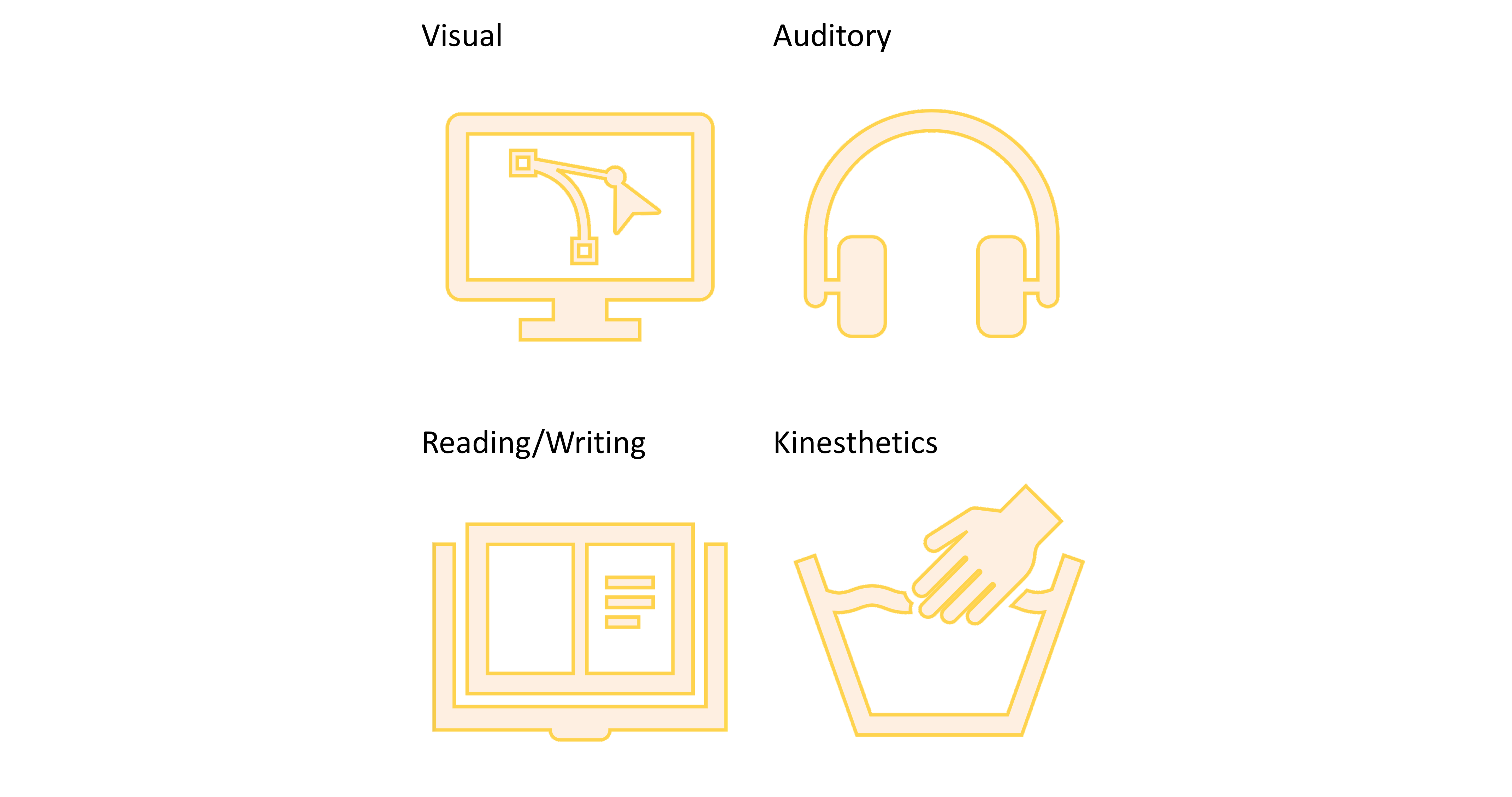

Visual
Visual learners understand and retain information best by seeing. The graphic displays may include illustrations, graphs, diagrams, movies, videos, image-laden handouts, color-coded notes, and so on.
Audio
Learners in this category assimilate the information better by hearing it. Podcasts, audiobooks or class recordings, songs, and mnemonics are helpful learning mediums in this category.
Read/Write
Some people learn better by reading and writing information. They find online or offline books, notes, and presentations more effective in understanding a concept.
Kinesthetics
Kinesthetic learners gain knowledge by practically doing things. These activities could be experiments, the creation of flashcards, presentations, project construction, etc.
Gamification in eLearning becomes a confluence point for all these learning styles.
“Games aren’t just filler in education. They have the ability to introduce, reinforce, or even assess learning of a given topic.” – Kara Carrero
VARK In Gamification For An Impactful Virtual Training Solution
Visual
Gamification provides wide scope for a rich visual feast. The videos or images for scenarios, points/scores, badges, progress bars, etc. help to create a visual matrix.



Audio
Gamification includes voiceovers both for instructions and the storyline. There could be audio clips for describing the scenarios or to give cues for the learner to choose an action.

Read/Write
In addition to online screen text, forums, real-time performance feedback, activity feeds, quizzes, etc. highlight the read-and-write aspect of the VARK model.

Kinesthetics
Activities in eLearning enhance personalized learning experiences. It could include games like “Scrabble,” finding the words, etc. Additionally, the learner’s choice of action could define the movement of the storyline.
There can be an activity to check the learner’s understanding before enforcing the knowledge itself. For example, the following activity lets the learner explore the understanding of equity and equality before listing them out, unlike in the traditional eLearning method.
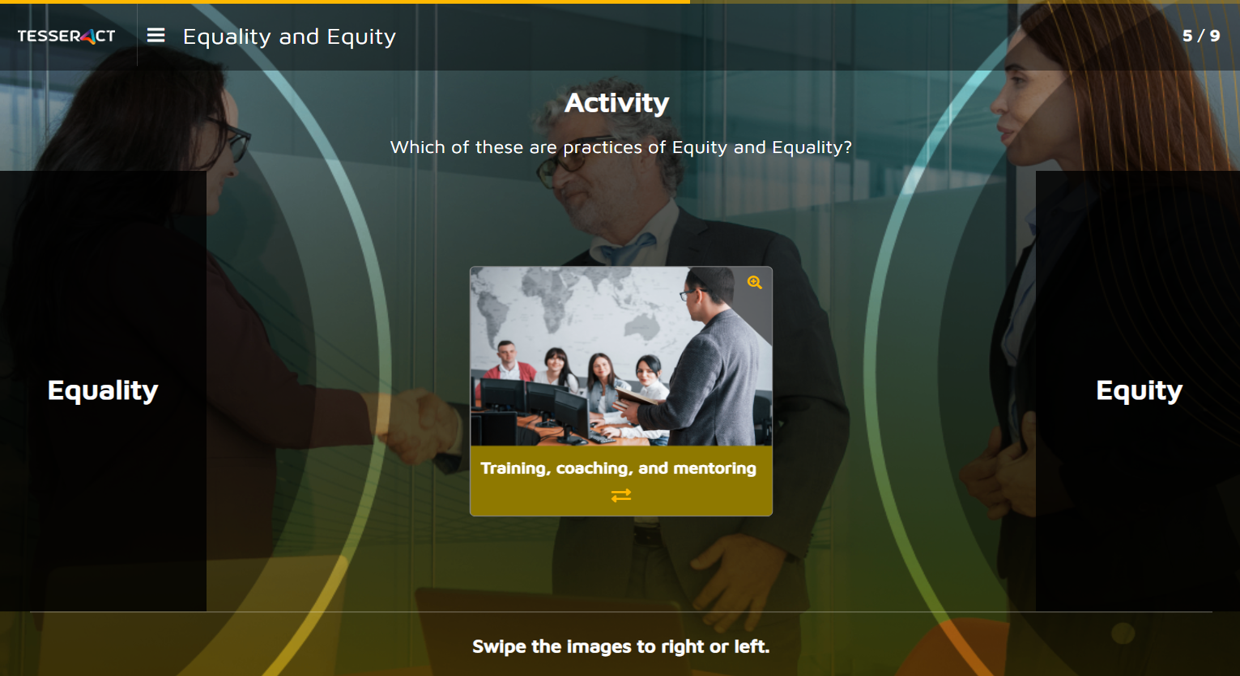
There is no end to the list of activities to engage the learner through gamification in eLearning.

Gamification has all the characteristics that appeal to learners as specified in the VARK model. Organizations can customize the proportion of visuals, audio, text, and activities depending on the need of the topic.
Corporate compliance training, products and services training, and skills development training are a good fit for the use of gamification in eLearning as a virtual training solution.
“Scientists have recently determined that it takes approximately 400 repetitions to create a new synapse in the brain—unless it’s done with play, in which case, it takes between 10 and 20 repetitions!” – Dr. Karen Purvis
Summary: With ever-increasing workplace training costs, it is a challenge to devise a virtual training solution that is engaging for all employees. In this article, we will explore the effectiveness of gamification in eLearning to deliver unparalleled training experiences across all learning styles.
Also read latest article on Examples of Microlearning.
How To Deliver Effective eLearning Gamification
Τhe average spending on workplace training per employee worldwide in 2019 was $1308. The companies aim to carve out a training program that reduces the learning curve and increases ROI. A dynamic virtual training solution should cater to everyone’s training needs and learning styles.
The use of gamification in eLearning makes the corporate training module highly effective. It is found engaging by many employees irrespective of their learning style.
Gamification In eLearning
Let’s get to know about the gaming elements in eLearning. The common concepts are game-based learning and gamification, which are sometimes used interchangeably by many of us. However, there is a difference.
Game-based learning refers to an active learning experience within a game framework. In comparison, gamification is a process of incorporating game elements into the virtual training solution. Both game-based learning and gamification help to increase engagement and training outcomes.
“Play is our brain’s favorite way of learning,” said poet, essayist, and naturalist Diane Ackerman.
Therefore, it is not surprising that the majority of employees find gamification in eLearning more engaging and motivating. There is no better way of motivation than the experience of joy in what we do. The same applies to corporate learning and no other method can bring more joy than gamification.
But what makes gamification in eLearning a favorite among people with varied learning styles? We will take into consideration the VARK model to understand this aspect. Gamification caters to all learning styles as elucidated by the VARK model.
VARK Model
The VARK model identifies four main types of learners based on their learning styles: visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic. It was introduced by educational theorist Neil Fleming in 1987. VARK stands for Visual, Aural, Reading, and Kinesthetic. Let’s look into each of them.

Visual
Visual learners understand and retain information best by seeing. The graphic displays may include illustrations, graphs, diagrams, movies, videos, image-laden handouts, color-coded notes, and so on.
Audio
Learners in this category assimilate the information better by hearing it. Podcasts, audiobooks or class recordings, songs, and mnemonics are helpful learning mediums in this category.
Read/Write
Some people learn better by reading and writing information. They find online or offline books, notes, and presentations more effective in understanding a concept.
Kinesthetics
Kinesthetic learners gain knowledge by practically doing things. These activities could be experiments, the creation of flashcards, presentations, project construction, etc.
Gamification in eLearning becomes a confluence point for all these learning styles.
“Games aren’t just filler in education. They have the ability to introduce, reinforce, or even assess learning of a given topic.” – Kara Carrero
VARK In Gamification For An Impactful Virtual Training Solution
Visual
Gamification provides wide scope for a rich visual feast. The videos or images for scenarios, points/scores, badges, progress bars, etc. help to create a visual matrix.



Audio
Gamification includes voiceovers both for instructions and the storyline. There could be audio clips for describing the scenarios or to give cues for the learner to choose an action.

Read/Write
In addition to online screen text, forums, real-time performance feedback, activity feeds, quizzes, etc. highlight the read-and-write aspect of the VARK model.

Kinesthetics
Activities in eLearning enhance personalized learning experiences. It could include games like “Scrabble,” finding the words, etc. Additionally, the learner’s choice of action could define the movement of the storyline.
There can be an activity to check the learner’s understanding before enforcing the knowledge itself. For example, the following activity lets the learner explore the understanding of equity and equality before listing them out, unlike in the traditional eLearning method.

There is no end to the list of activities to engage the learner through gamification in eLearning.

Gamification has all the characteristics that appeal to learners as specified in the VARK model. Organizations can customize the proportion of visuals, audio, text, and activities depending on the need of the topic.
Corporate compliance training, products and services training, and skills development training are a good fit for the use of gamification in eLearning as a virtual training solution.
“Scientists have recently determined that it takes approximately 400 repetitions to create a new synapse in the brain—unless it’s done with play, in which case, it takes between 10 and 20 repetitions!” – Dr. Karen Purvis